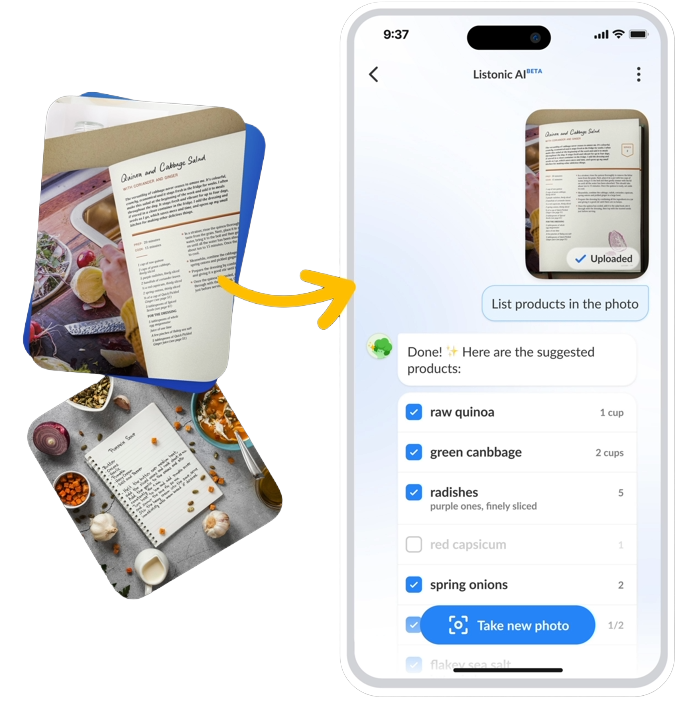
The Challenge
Despite being the leading shopping list app, we identified a friction point: the manual effort of digitizing recipes from cookbooks or handwritten notes. User feedback and support tickets pointed toward a need for a “faster way to add items.”
The goal was to build a low-cost, high-impact AI prototype to test user appetite for LLM-integrated features and to “warm up” our technical stack for AI implementation.
My Strategy & Actions: A Methodological Shift
As the Lead PM, I architected a product framework designed to bridge the gap between high-risk AI experimentation and scalable delivery:
- Introducing Shape Up Methodology: To foster the creativity required for AI, I moved the team away from rigid sprints toward a Shape Up-inspired framework. This allowed for better “appetite” setting and gave the team the autonomy to voice creative solutions regardless of their domain.
- Iterative Feedback Loop: Instead of waiting for a final release, I collected structured internal feedback through surveys and interviews after every milestone, ensuring the LLM’s behavior aligned with our brand voice.
- Mitigating AI Hallucinations: To manage the inherent uncertainty of LLM outputs, I designed a Three-Mode Logic to set proper user expectations:
- Recognition Mode: High-precision extraction of ingredients from recipes.
- Suggestion Mode: Analyzing a photo of a shopping cart to suggest missing staples.
- Inspiration Mode: A creative “vibe-check” that generates recipes based on the mood of a photo (e.g., a forest photo suggesting “wild mushroom risotto”).
The Results: Lessons in Product-Market Fit
The project delivered significant value, although the user data provided a reality check:
- Process Success: The Shape Up approach was so effective that it was adopted as the standard for other exploratory projects, improving cross-departmental collaboration and development velocity.
- Technical Readiness: We successfully integrated LLMs into our stack, establishing a blueprint for all future AI-driven features in the Listonic ecosystem.
- User Sentiments: While the feature remained a niche tool (used by <5% of the user base), the qualitative feedback was strong. 75% of active users rated the feature as “highly useful,” proving the solution worked well for its specific target group.
- Data-Driven Pivots: The project taught us that AI features need stronger UI/marketing exposure and broader pre-development validation. These insights are now the foundation for our upcoming AI roadmap.
Summary
AI Vision was a strategic success in risk management and R&D. We validated a niche problem, learned the nuances of LLM integration, and revolutionized our internal development culture. It proved that sometimes, the most valuable outcome of a feature is the institutional knowledge and operational efficiency it leaves behind.